- About Congenital Heart Disease
About Congenital Heart Disease
About 9 babies in every 1,000 born in the Philippines will have a problem with their heart or major blood vessels.
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as acongenital heart anomaly or congenital heart disease, is a problem in the structure of the heart that is present at birth. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of problem.
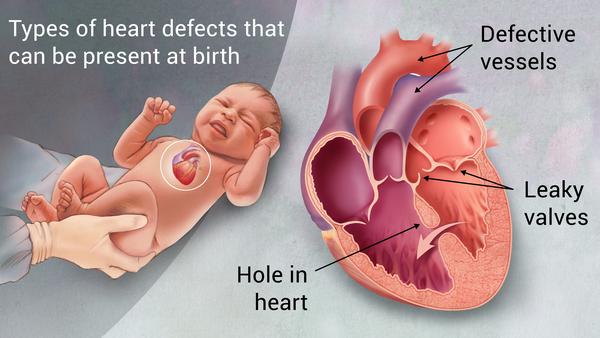
Major types of CHD
Introduction: Understanding Congenital Heart Defects
Source: American Heart Association website
About CHD
The word “congenital” means existing at birth. The terms “congenital heart defect” and “congenital heart disease” are often used to mean the same thing, but “defect” is more accurate. The heart ailment is a defect or abnormality, not a disease. A defect results when the heart or blood vessels near the heart don’t develop normally before birth.
If your child is born with a heart defect today, the chances are better than ever that the problem can be overcome and that a normal adult life will follow. Recent progress in diagnosis and treatment (surgery and heart catheterization) makes it possible to fix most defects, even those once thought to be hopeless. As diagnosis and treatment continue to advance, scientists will develop treatments for other defects.
After your child is diagnosed with a congenital heart defect, more tests may be needed. They’ll help the children’s heart specialist (pediatric cardiologist) and the surgeon to decide whether a treatment (surgery or heart catheterization) is a good idea. But before that point is reached, you can learn a lot to make the best use of the help available to you.
About Congenital Heart Disease
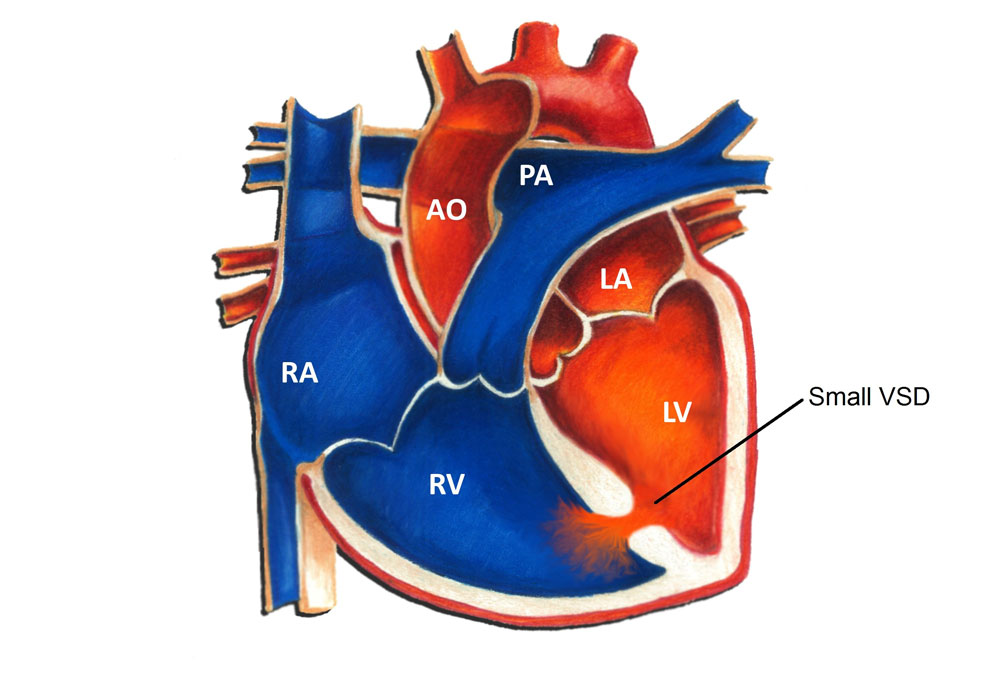
Most Common Types of CHD
Ventricular septal defect (VSD), atrial septal defects, and tetralogy of Fallot are the most common congenital heart defects.
Ventricular Septal Defect
Ventricular septal defect (VSD): A hole in the septum (the wall) between the lower chambers of the heart (the ventricles). Ventricular Septal Defect is the most common type of heart malformation (congenital heart disease). At least 1 baby in every 500 is born with a VSD.
Atrial Septal Defect
A "hole" in the wall that separates the top two chambers of the heart. This defect allows oxygen-rich blood to leak into the oxygen-poor blood chambers in the heart. ASD is adefect in the septum between the heart's two upper chambers (atria).
Tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a type of heart defect present at birth. Symptoms include episodes of bluish color to the skin. When affected babies cry or have a bowel movement, they may develop a "tet spell" where they turn very blue, have difficulty breathing, become limp, and occasionally lose consciousness. Other symptoms may include a heart murmur, finger clubbing, and easy tiring upon breastfeeding.

Accordint to Children's Heartlink
Worldwide, 90% of children with heart disease don’t have access to the care they need.
To understand more obout CHD worldwide you may want to read publications from Childrens's Heartlink:
The Invisible Child: Childhood Heart Disease and the Global Health Agenda
Invisible Child Series
In this series you can learn about children mortality rate and share of CHD on it.

